Getting Started#
Installation#
The Geometry Analysis step is probably already installed in your SEAMM environment, but if not or if you wish to check, follow the directions for the SEAMM Installer. The graphical installer is the easiest to use. In the SEAMM conda environment, simply type:
seamm-installer
or use the shortcut if you installed one. Switch to the second tab, Components, and check for geometry-analysis-step. If it is not installed, or can be updated, check the box next to it and click Install selected or Update selected as appropriate.
The non-graphical installer is also straightforward:
seamm-installer install --update geometry-analysis-step
will ensure both that it is installed and up-to-date.
Examining a structure#
This simple flowchart download
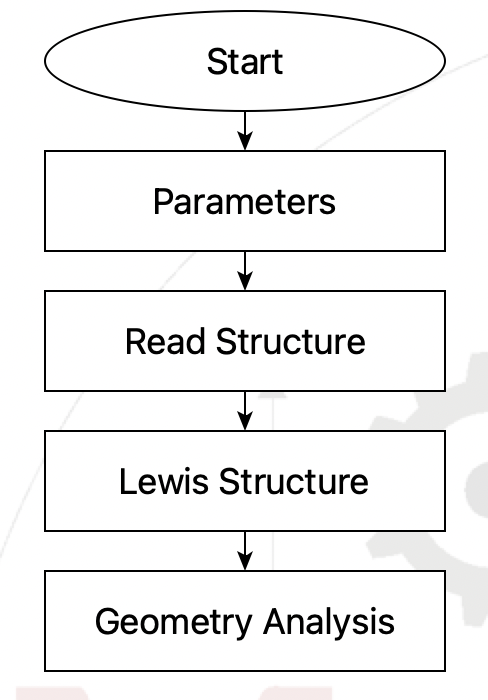
Flowchart for simple geometry analysis#
will read a molecular structure file, add bonds using the MOPAC functionality for generating the Lewis structure, then print information about the bonds, angles, etc.
Runing the flowchart on a structure of water – the XYZ file
from the DFTB+ distribution in this example – yields the following output:
Step 4: Geometry Analysis 2022.12.24
Tabulate the bond lengths, angles, dihedral angles, and Wilson out-of-plane
angles for the system.
Number of atoms: 3
Bonds
+-------+------+-----------+
| Atoms | Bond | Value (Å) |
+-------+------+-----------+
| 2-1 | H-O | 0.9672 |
| 3-1 | H-O | 0.9672 |
+-------+------+-----------+
Angles
+-------+-------+-----------+
| Atoms | Angle | Value (º) |
+-------+-------+-----------+
| 3-1-2 | H-O-H | 107.19 |
+-------+-------+-----------+
There are no dihedrals in this system.
There are no out-of-planes in this system.
A slightly more complex example, 1,2-butadiene
H2C=C=CH-CH3 from MOPAC:
Step 4: Geometry Analysis 2022.12.24
Tabulate the bond lengths, angles, dihedral angles, and Wilson out-of-plane
angles for the system.
Number of atoms: 10
Bonds
+-------+------+-----------+
| Atoms | Bond | Value (Å) |
+-------+------+-----------+
| 2-1 | C=C | 1.3008 |
| 3-2 | C=C | 1.3059 |
| 4-8 | C-H | 1.0985 |
| 1-5 | C-H | 1.0817 |
| 4-3 | C-C | 1.4905 |
| 4-9 | C-H | 1.1002 |
| 1-6 | C-H | 1.0817 |
| 3-7 | C-H | 1.0914 |
| 4-10 | C-H | 1.1002 |
+-------+------+-----------+
Angles
+--------+-------+-----------+
| Atoms | Angle | Value (º) |
+--------+-------+-----------+
| 2-1-5 | C=C-H | 123.58 |
| 2-1-6 | C=C-H | 123.58 |
| 6-1-5 | H-C-H | 112.84 |
| 3-2-1 | C=C=C | 180.00 |
| 4-3-2 | C-C=C | 122.84 |
| 2-3-7 | C=C-H | 121.43 |
| 4-3-7 | C-C-H | 115.73 |
| 3-4-8 | C-C-H | 112.69 |
| 3-4-9 | C-C-H | 110.94 |
| 3-4-10 | C-C-H | 110.94 |
| 9-4-8 | H-C-H | 107.31 |
| 10-4-8 | H-C-H | 107.31 |
| 10-4-9 | H-C-H | 107.41 |
+--------+-------+-----------+
Dihedral Angles
+----------+----------+-----------+---------------------+
| Atoms | Dihedral | Value (º) | Description |
+----------+----------+-----------+---------------------+
| 3-2-1-5 | C=C=C-H | 0.00 | C = synperiplaner |
| 3-2-1-6 | C=C=C-H | 0.00 | C = synperiplaner |
| 4-3-2-1 | C-C=C=C | 0.00 | C = synperiplaner |
| 1-2-3-7 | C=C=C-H | 0.00 | C = synperiplaner |
| 2-3-4-8 | C=C-C-H | 0.00 | C = synperiplaner |
| 2-3-4-9 | C=C-C-H | 120.35 | A+ = +anticlinal |
| 2-3-4-10 | C=C-C-H | -120.35 | G- = -synclinal |
| 8-4-3-7 | H-C-C-H | 180.00 | T = antiperiplaner |
| 9-4-3-7 | H-C-C-H | -59.65 | G- = -synclinal |
| 10-4-3-7 | H-C-C-H | 59.65 | G+ = +synclinal |
+----------+----------+-----------+---------------------+
Out-of-plane Angles
+-----------+-----------+-----------+
| Atoms | Oop | Value (º) |
+-----------+-----------+-----------+
| 2-1(-5)-6 | C=C(-H)-H | 0.00 |
| 2-3(-4)-7 | C=C(-C)-H | 0.00 |
+-----------+-----------+-----------+
That should be enpugh to get started. However, remember that this functionality depends on having bonds in the structure, so you either need to use file formats that support bond information, start from SMILES, or, as we did here, use one of the tools in SEAMM to create the appropriate bonding information.
For more detail about the functionality in this plug-in, see the User Guide.